Determine the isotope symbol that fits each description – In the realm of science, the ability to accurately identify and represent isotopes is crucial. Isotope symbols provide a concise and systematic method for conveying the unique characteristics of these atomic variants. This article delves into the significance of isotope symbols, their composition and conventions, and their wide-ranging applications across scientific disciplines.
Isotope Symbol Identification: Determine The Isotope Symbol That Fits Each Description
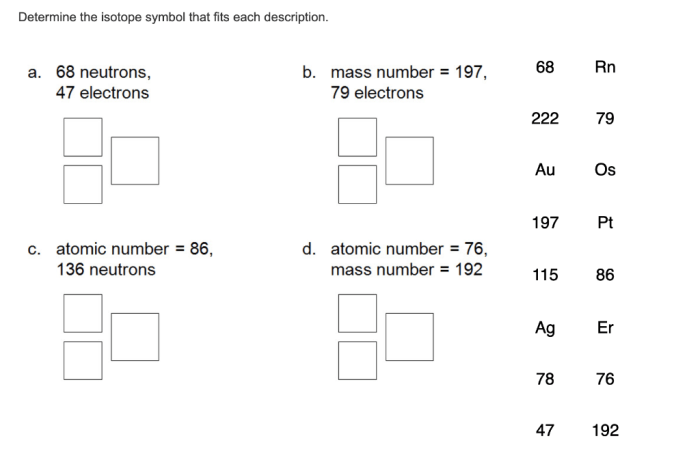
Isotope symbols are a shorthand notation used to represent isotopes, which are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. This notation is essential for easily identifying and distinguishing between different isotopes.
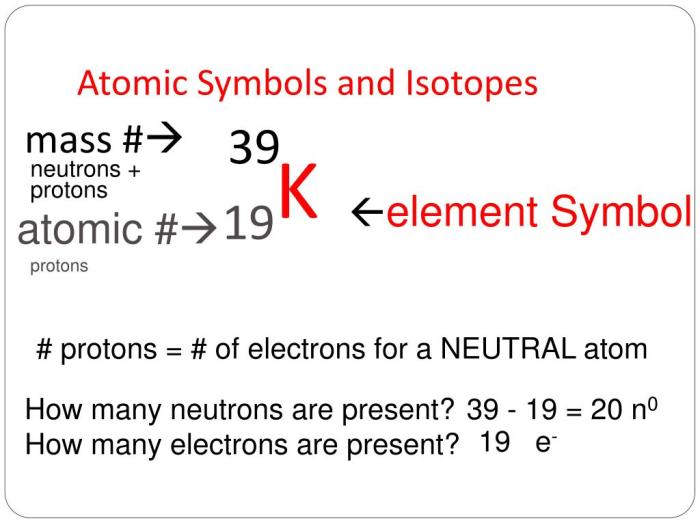
The isotope symbol consists of the chemical symbol of the element, followed by a superscript indicating the mass number and a subscript indicating the atomic number. For example, the isotope symbol for carbon-12 is 12C, where 12 is the mass number and 6 is the atomic number.
| Isotope Name | Isotope Symbol | Number of Protons | Number of Neutrons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen-1 | 1H | 1 | 0 |
| Hydrogen-2 (Deuterium) | 2H | 1 | 1 |
| Carbon-12 | 12C | 6 | 6 |
| Carbon-14 | 14C | 6 | 8 |
| Oxygen-16 | 16O | 8 | 8 |
Isotope Symbol Characteristics
The composition of isotope symbols includes two key components: the atomic number and the mass number.
- Atomic Number:The atomic number represents the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. It is written as a subscript before the chemical symbol.
- Mass Number:The mass number represents the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. It is written as a superscript before the chemical symbol.
Superscripts and subscripts are used in isotope symbols to distinguish between different isotopes of the same element. For example, 1H and 2H both represent isotopes of hydrogen, but they have different mass numbers, indicating different numbers of neutrons.
Here are some examples of isotope symbols for different elements:
- Hydrogen: 1H, 2H, 3H
- Carbon: 12C, 13C, 14C
- Oxygen: 16O, 17O, 18O
Isotope Symbol Applications
Isotope symbols are widely used in various scientific fields, including chemistry, physics, and medicine.
- Chemistry:Isotope symbols are used to identify and track different isotopes of elements in chemical reactions and isotopic analysis.
- Physics:Isotope symbols are used in nuclear physics to study the properties and interactions of isotopes.
- Medicine:Isotope symbols are used in medical imaging and cancer treatment to track radioactive isotopes, such as 99mTc and 131I.
In research and industry, isotope symbols are used to:
- Identify and characterize different isotopes in materials
- Study the behavior and properties of isotopes in various environments
- Develop and optimize processes that involve isotopes
Isotope Symbol Conventions

There are established rules and conventions for writing isotope symbols:
- The chemical symbol of the element is always written first.
- The mass number is written as a superscript before the chemical symbol.
- The atomic number is written as a subscript before the chemical symbol.
- For radioactive isotopes, the atomic number and mass number are separated by a hyphen.
- For isotopes with the same mass number but different atomic numbers, the atomic number is written as a subscript before the chemical symbol, followed by a hyphen and the mass number.
Here are some examples of isotope symbols written according to these conventions:
- 12C (carbon-12)
- 14C (carbon-14)
- 99mTc (technetium-99m)
- 131I- (iodine-131)
FAQ Guide
What is the purpose of using isotope symbols?
Isotope symbols provide a standardized and concise way to represent the isotopic composition of elements, facilitating communication and understanding among scientists.
How are isotope symbols composed?
Isotope symbols consist of the element symbol, followed by a superscript indicating the mass number (total number of protons and neutrons) and a subscript indicating the atomic number (number of protons).
What are some examples of isotope symbols?
Examples of isotope symbols include 12C for carbon-12, 14N for nitrogen-14, and 235U for uranium-235.